Model and meaning of encoder
Model and meaning of encoder
Encoder is a very common human-computer interaction information input component, which is mainly divided into two categories: one is photoelectric encoder and the other is contact coding
Today, I will mainly share with you the model and naming rules of the contact rotary encoder.

Many encoder manufacturers of this type do not have a unified industry standard for the encoder model and naming. They are all compiled by the manufacturers themselves.
Next, take the model of the rotary encoder in the figure below as an example, and give you an explanation of the model naming specification. The same applies to the rotary encoder naming convention then.
The following picture: RE1103IC1-H01-0006 (15P30, AA9F4) This is a typical complete encoder model
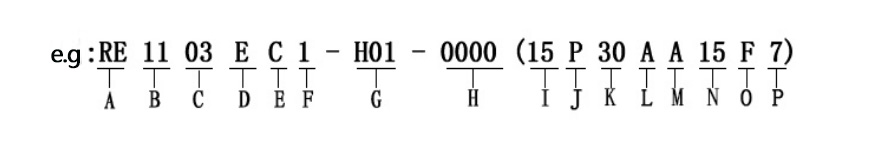
A: RE is the code name of the encoder, the naming rules of the manufacturer are different, the previous code is also different. Lin Jiwei takes RE is the rotary encoder rotary
Encoder English initials.
B: The key size of appearance 11 is about 11mm of a certain surface.
C: 03 is a thin base with switch products, there are also products such as 00 thick base without switch, 01 thick base with switch and so on.
D: The shape code of the shaft sleeve, I is the 3.5mm length unthreaded shaft sleeve, and there are 7mm, 5mm, 10mm thread and other information.
E: bracket code, C bracket represents the installation method is plug-in method, the width of the bracket foot is 2.0mm, the total span of the bracket foot is 13.2mm, and the width
2.5mm span 12.9 with patch bracket feet and so on.
F: Represents whether the bottom cover has positioning posts, 1 represents no posts. There are also 2 means there are two positioning columns, 3 means there are two large positioning columns and so on.
G: terminal pin type, H01 stands for vertical plug-in pin. There are also V01 and other parameters such as the number of terminal pins, terminal pin shape, and terminal pin span.
H: Internal serial number, the information represented is reflected in parentheses.
I: The number of pulses, which represents the pulse information of the product. The number of pulses for different types of encoders is different, such as: 9 pulses, 12 pulses, 15 pulses, 20 pulses, 24 pulses and so on.
J: The direction of pulse output, which represents whether the pulse is output through forward or reverse rotation. P represents clockwise rotation and T represents counterclockwise rotation.
K: The number of positioning, which represents how many positioning points there are in this rotation, which is the sense of gear. The number of positioning and the number of pulses must appear in a ratio of 1:1 or 2:1.
L: the shape of the shaft core, A represents the D-shaped half shaft, K represents the quincunx garland shaft and so on.
M: stands for shaft core material, A stands for aluminum alloy material, B stands for zinc alloy material, C stands for copper material, D stands for stainless steel material, L stands for plastic material and so on.
N: 15 represents the actual installation height, the height from the PCB to the top.
O: F represents the opening direction of the shaft core, generally only the A-axis D-shaped half shaft will have
P: 7 represents the length of the operating part of the shaft, N and Q can be selected according to specific actual requirements.
The combination of the above codes can be regarded as a complete product model. The naming rules of each manufacturer are also different. In fact, only a few key information is needed for the buyer, especially the encoder model for new projects. You can directly give you a few requirements for the manufacturer to recommend to you is the best, if you are looking for a substitute, you need to go through detailed matching.
Absolute pulse encoder: APC incremental pulse encoder: SPC Both are generally used in speed control or position control system detection elements. Rotary encoder is a device used to measure speed. It is divided into two types: single output and dual output. Technical parameters mainly include the number of pulses per revolution (dozens to thousands of them), and power supply voltage.
Single output means that the output of the rotary encoder is a set of pulses, while the dual output rotary encoder outputs two sets of pulses with a phase difference of 90 degrees. The two sets of pulses can not only measure the speed, but also determine the direction of rotation. The difference between incremental encoder and absolute encoder Encoders are divided into signal principle, there are incremental encoders, absolute encoders.
Incremental encoder (rotary type) working principle: It consists of a photoelectric code disc with a shaft in the center, on which there are circular and dark engraved lines, and there are photoelectric emission and connection
The receiving device reads and obtains four groups of sine wave signals combined into A, B, C, D, each sine wave has a phase difference of 90 degrees (relative to a cycle of 360 degrees), the C and D signals are reversed and superimposed on On A and B phases, the stable signal can be enhanced; in addition, a Z-phase pulse is output per revolution to represent the zero reference position.

Since the phases A and B differ by 90 degrees, the encoder's forward and reverse rotation can be judged by comparing the phase A or the B phase. The zero reference position of the encoder can be obtained through the zero pulse. The materials of the encoder code disc are glass, metal, plastic. The glass code disc is deposited on the glass with very thin scribe lines, which has good thermal stability and high precision. The metal code disc is directly engraved with through and impassable lines and is not fragile. However, due to the certain thickness of metal, the accuracy is limited, and its thermal stability is one order of magnitude worse than that of glass. Plastic code discs are economical, and their cost is low, but accuracy, thermal stability, and life are worse. . Resolution—The number of open or dark engraved lines provided by the encoder per 360 degree rotation is called resolution, also called resolution indexing, or directly called the number of lines, generally 5 to 10,000 lines per revolution.
Signal output: The signal output has sine wave (current or voltage), square wave (TTL, HTL), open collector (PNP, NPN), push-pull multiple forms, among which TTL is a long-line differential drive (symmetrical A, A-; B, B-; Z, Z-), HTL is also called push-pull, push-pull output, the signal receiving device interface of the encoder should correspond to the encoder. Signal connection—The pulse signal of the encoder is generally connected to the counter, PLC, and computer. The modules connected to the PLC and the computer are divided into low-speed modules and high-speed modules, and the switching frequency is low or high.
Such as single-phase connection, used for single direction counting and single direction speed measurement. A.B two-phase connection, used for forward and reverse counting, judgment of forward and reverse and speed measurement. A, B, Z three-phase connection, used for position measurement with reference position correction. A, A-, B, B-, Z, Z- connections, due to the connection with symmetrical negative signals, the electromagnetic field contributed by the current to the cable is 0, the attenuation is the smallest, the anti-interference is the best, and it can be transmitted over a long distance. For TTL encoders with symmetrical negative signal output, the signal transmission distance can reach 150 meters. For HTL encoders with symmetrical negative signal output, the signal transmission distance can reach 300 meters.





