Principle and Application of Rotary Encoder
Principle and Application of Rotary Encoder
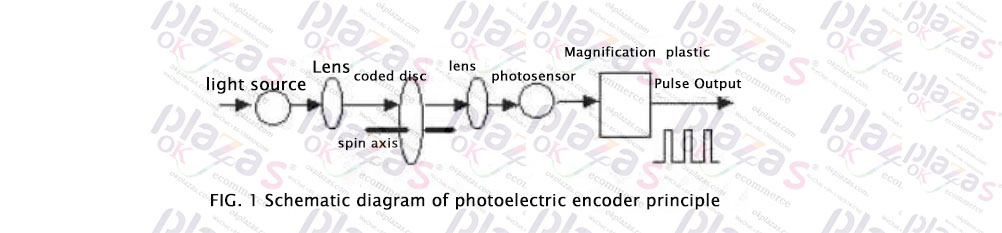
The rotary encoder converts the timing and phase relationship of its angle code disc through two internal photosensitive receiving tubes, and obtains the increase (positive direction) or decrease (negative direction) of the angular displacement of the angle code disc. After joining the digital circuit, especially the single-chip microcomputer, the incremental rotary encoder has the advantages of cheaper and simpler than the absolute rotary encoder in angle measurement and angular velocity measurement. The following is the internal working principle of the incremental rotary encoder (with photos)
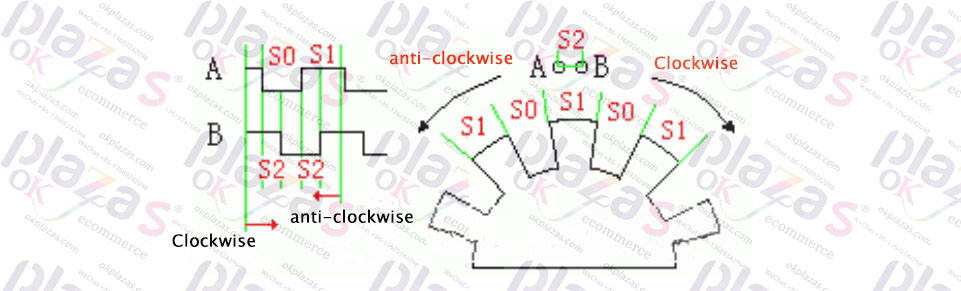
Rotary encoder principle
The two points A and B correspond to two photosensitive receiving tubes, the distance between the two points A and B is S2, and the grating distance of the angle code disc is S0 and S1 respectively.
When the angle code wheel rotates at a constant speed, it can be seen that the ratio of S0:S1:S2 in the output waveform diagram is the same as the ratio of S0:S1:S2 in the actual diagram. Similarly, when the angle code wheel rotates at a constant speed at other speeds, The ratio of S0:S1:S2 in the output waveform diagram is still the same as the ratio of S0:S1:S2 in the actual diagram. If the angle code wheel makes a variable-speed motion, and regard it as a combination of multiple motion cycles (defined below), then the ratio of S0:S1:S2 in the output waveform diagram in each motion cycle is compared to the S0:S1:S2 in the actual diagram. The ratio remains the same.
The output waveform chart shows that the timing of each motion cycle is
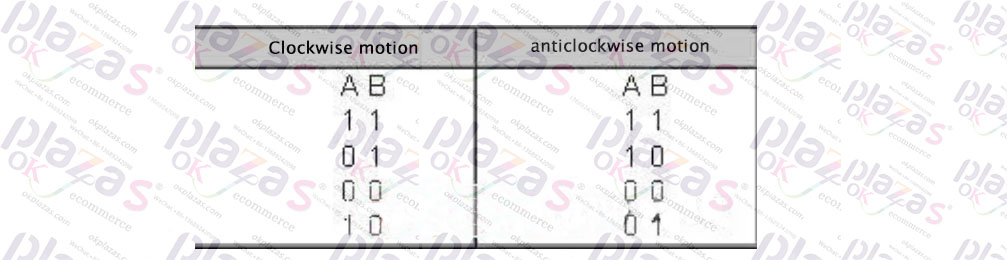
We save the current output values of A and B and compare them with the next output values of A and B, and then we can easily get the direction of motion of the angle code wheel.
If the optical grid S0 is equal to S1, that is, the angle between S0 and S1 radians is the same, and S2 is equal to 1/2 of S0, then the displacement angle of this angular code disc movement is 1/2 of the included angle of S0 radians, divided by The angular velocity of the movement of this angular code disc can be obtained in the time that is lost.
When S0 is equal to S1, and S2 is equal to 1/2 of S0, the movement direction and displacement angle can be obtained in 1/4 of the movement cycle. If S0 is not equal to S1 and S2 is not equal to 1/2 of S0, then 1 The movement direction and displacement angle can be obtained by the movement period.
The mouse we commonly use is also based on this principle.
Classification of rotary encoders
According to the detection principle, rotary encoders can be divided into optical, magnetic, inductive and capacitive. According to its scale method and signal output form, it can be divided into three types: incremental, absolute and hybrid.
1.1 Incremental encoder
Incremental encoders directly use the principle of photoelectric conversion to output three sets of square wave pulses A, B and Z phases; A and B pulses have a phase difference of 90°, so that the direction of rotation can be easily judged, and the Z phase is per revolution One pulse is used for reference point positioning. Its advantages are simple structure, average mechanical life of more than tens of thousands of hours, strong anti-interference ability, high reliability, and suitable for long-distance transmission. The disadvantage is that the absolute position information of the shaft rotation cannot be output.
Classification and selection of photoelectric encoders
The photoelectric encoder uses the principle of grating diffraction to realize displacement-digital conversion. It has been applied to machine tools and computing instruments since the 1950s. Because of its simple structure, high measurement accuracy, and long life, it has received attention and promotion at home and abroad. In recent years, it has made considerable progress and has been widely used in precision positioning, speed, length, acceleration, and vibration.
Photoelectric encoders are divided into two categories according to encoding methods: incremental and absolute.
1. Features of incremental encoder:
When the shaft of the incremental encoder rotates, there is a corresponding pulse output, and its counting starting point is set arbitrarily, which can realize multi-turn infinite accumulation and measurement. One rotation of the encoder shaft will output a fixed pulse, and the number of pulses is determined by the number of encoder grating lines. When you need to improve the resolution, you can use the A and B signals with a 90-degree phase difference to multiply the frequency or replace the high-resolution encoder.
2. Features of absolute encoder:
Absolute encoders have a DEMA output corresponding to the position, usually binary code or BCD code. From the change of the code number, the positive and negative directions and the position of the displacement can be judged. The absolute zero code can also be used for power failure position memory. The measuring range of absolute encoder is usually 0-360 degrees.
Application of rotary encoder
Speedometers and length meters generally use incremental encoders. The following briefly introduces their parameter ranges for reference for selection.
(1)Number of grating lines:

(2) Output method:
There are five conventional output methods:
Open collector output (universal type)
Complementary output
Voltage output
Long line driver output
UVW output
(3) Working voltage: Conventionally, there are the following:
5V, 12V, 24V, 5-24V (universal type), 5-30V
(4) Protection performance: conventionally oil-proof, dust-proof and shock-proof.
(5) Elastic coupling: When the encoder shaft is connected with the user shaft, there is a coaxial error, which will damage the encoder in severe cases. It is required to use elastic couplings (encoder manufacturers provide options) to solve the problem of eccentricity. Generally, the allowable torque is "1N.m, the different axis degree is "0.2mm, the axial deflection angle is "1.5 degrees.
Common specifications of elastic couplings are:
(6) Installation and precautions:
Rotary encoders are high-precision instruments, and must not be knocked or bumped during installation. The shaft end connection should avoid rigid connection, but should adopt elastic coupling, nylon gear or timing belt to connect and drive. The operating speed should not exceed the nominal speed, otherwise the electrical signal will be affected.





