Resolution, frequency multiplication and subdivision of incremental encoder
Resolution, frequency multiplication and subdivision of incremental encoder
Resolution, frequency multiplication and subdivision of incremental encoder
Incremental encoder code disc is composed of many grating lines. There are two (or 4, 4 optical eyes will be discussed later) optical eyes to read A and B signals. The density of the engraved lines determines this increment. The resolution of the type encoder is the smallest change angle value that can be read. The parameter representing the resolution of the incremental encoder is PPR, which is the number of pulses per revolution, for example, 360 lines per revolution, A and B output 360 pulses per revolution, and the resolution parameter is 360PPR.
So what is the minimum angular change that this encoder can distinguish? Is it 1 degree?
The A/B output waveforms of incremental encoders generally have two types, one is a square wave signal with a steep rising edge and a steep falling edge, and the other is a Sin/Cos with a slow rise and fall, and the waveform is similar to a sine curve. Curved waveform signal output, A and B have a phase difference of 1/4T period of 90 degrees. If A is a sine-like Sin curve, then B is a cosine-like Cos curve.
For a square wave signal, the phases A and B differ by 90 degrees (1/4T). Thus, at the phase angles of 0 degrees, 90 degrees, 180 degrees, and 270 degrees, these four positions have rising and falling edges. In this way, in fact, the angle change can be judged in the period of 1/4T square wave, so that the 1/4 T period is the minimum measurement step. Through the circuit's judgment on these rising and falling edges, it can be read by 4 times the PPR Taking the change of angle, this is the quadruple frequency of the square wave. This kind of judgment can also be made with logic. 0 stands for low, 1 stands for high, and the A/B phase changes in one cycle to 0 0,0 1,1 1,1 0. This judgment can not only 4 times the frequency, but also the direction of rotation.
Then, the minimum resolution angle of the square wave signal = 360 degrees/(4xPPR).
The previous question: a square wave A/B output 360PPR incremental encoder, the minimum resolution angle = 0.25 degrees.
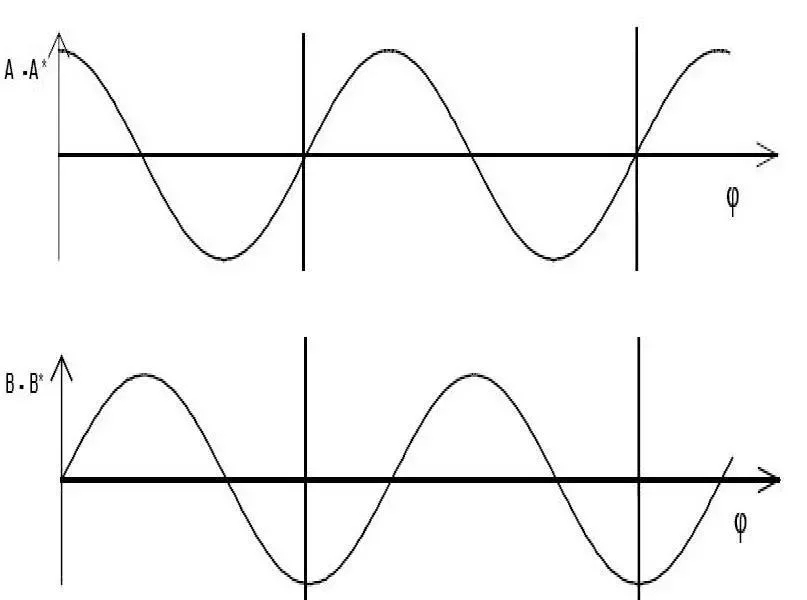
Strictly speaking, the square wave can only be multiplied by 4 times. Although some people can use the time difference method to divide more finely, it is basically not recommended by the incremental encoder. For higher frequency divisions, the incremental pulse signal is SIN/ COS-like sine and cosine signals, the subsequent circuit can read the phase change of the waveform, and use the analog-to-digital conversion circuit to subdivide, 5 times, 10 times, 20 times, or even more than 100 times, and then use the square wave after dividing. Waveform output (PPR). The multiplier of the frequency division is actually limited. First of all, the analog-to-digital conversion has time response problems. The speed of the analog-to-digital conversion and the accuracy of resolution are a contradiction. It is impossible to subdivide infinitely. If the division is too fine, the response and accuracy There is a problem; secondly, the reticle accuracy of the original encoder, the consistency of the output sine-cosine signal itself, and the perfection of the waveform are limited. If the division is too fine, it will only expose the error of the original code disk more obviously, and bring error. Subdivision is easy to do, but it is difficult to do it well. On the one hand, it depends on the accuracy of the original code wheel and the perfection of the output waveform, and on the other hand, it depends on the response speed and resolution accuracy of the subdivision circuit. For example, for industrial encoders from Heidenhain, Germany, the recommended best subdivision is 20 times. A higher subdivision is its recommended angle encoder with higher accuracy, but the rotation speed is very low.
An incremental encoder that outputs A/B/Z square wave after subdivision can also be 4 times the frequency again, but please note that subdivision has requirements for the encoder's rotation speed, which is generally lower. In addition, if the marking accuracy of the original code disc is not high, the waveform is not perfect, or the limitation of the subdivision circuit itself, the subdivision may cause serious waveform distortion, large and small steps, lost steps, etc. Please pay attention when selecting and using.
The previous question: an incremental encoder with sine and cosine A/B output 360PPR, the minimum resolution angle may be 0.01 degrees (if the frequency is divided by 25 and the original code disc accuracy is guaranteed).
For some incremental encoders, the original reticle can be 2048 lines (2 to the 11th power, 11 bits). Through 16 times (4 bits) subdivision, 15 bits of PPR are obtained, and 4 times frequency (2 bits) is obtained again. The resolution is 17 bits (Bit), which is derived from the 17-bit high-digit encoder of some Japanese encoders. It generally uses "Bit, Bit" to express the resolution. When this kind of Japanese encoder is faster, it still uses the unsubdivided low-level signal to process the output, otherwise the response will not keep up, so don't be confused by its "17-bit".





