What are the common encoders on the market
What are the common encoders on the market
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts a signal (such as a bit stream) or data into a signal form that can be used for communication, transmission, and storage. The encoder converts angular displacement or linear displacement into electrical signals. The former is called a code wheel and the latter is called a code ruler. Encoders can be divided into contact type and non-contact type according to the reading mode; encoders can be divided into two types: incremental and absolute according to the working principle.
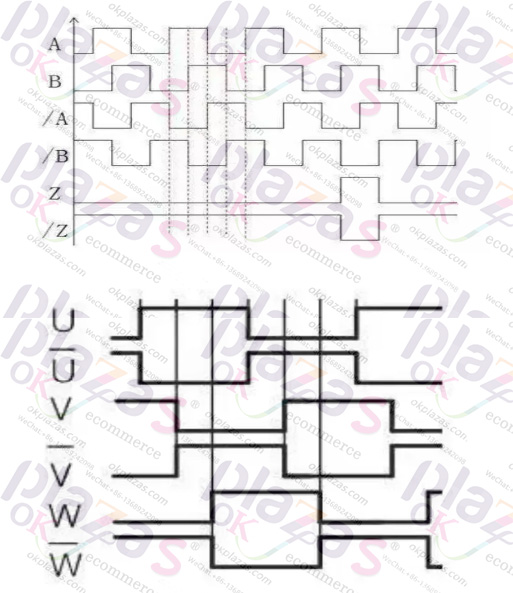
1.2500 line square wave pulse ABZ (including reverse phase), and UVW (including reverse) commutation signal. Among them, the square wave pulse signal of 2500 lines can reach the actual resolution of 10000/360 degrees after a quadruple frequency. It is the position and speed loop corresponding to the motor control, and UVW is the position commutation of the winding coil of the corresponding synchronous servo motor. There are 4 pairs of levels, 8 pairs of levels and more. This kind of encoder has a lot of output core wires, including two wires of the power supply, there are 14 core wires in total.
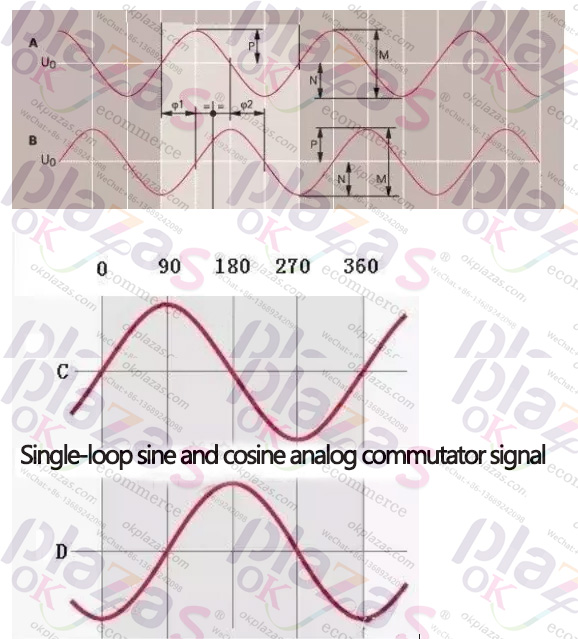
2.2048 line AB phase contains inverted sine and cosine signal output and single-turn cycle CD phase contains inverted sine and cosine signal. This requires the servo controller receiving device to subdivide the sine and cosine signals to obtain higher resolution (AB), and single-turn position (CD) to control the commutation.
The signal lines are A+A-, B+B-, C+C-, D+D-, and the power supply is positive and negative.
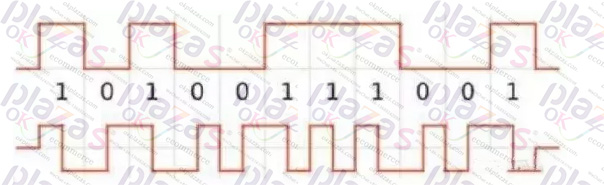
3.2048 line AB contains sine and cosine signals, plus digital serial signals.
For example, in the early hiperface1.0, the RS485 signal (RS485) obtains the UVW position of the motor rotor coil, and the incremental AB sine and cosine signal is selected when rotating. The servo controller receives the sine and cosine signal and subdivides into higher resolution (such as fine 10 digits, 2048×1024).
Or similar Endat2.1, RS422 signal + AB sine and cosine, or SSI, RS422 signal + AB sine and cosine.
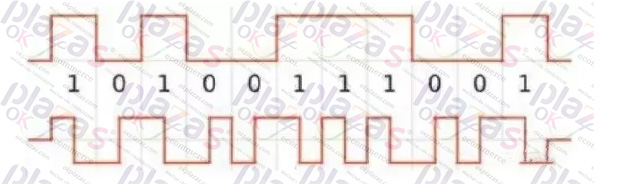
4. The sine and cosine signals of 2 above are subdivided and integrated into digital signals within the encoder, or the two sets of signals in 3 are combined into a set of serial digital signal output, providing 14 bits, 17 bits, 19 bits, 22 bits, 25 Bits and so on digital signals.
For example Endat2.2, Blss,
HiperFace, RS485,
EtherCat (or other bus type, Ethernet type signal), DSL and so on.
In the above-mentioned encoders with 17-bit-25-bit (single-turn) resolution, they do not refer to the accuracy of the encoder, but the resolution of the encoder. The same is a 17-bit encoder, which is likely to be accurate are different.
For example, the 17-bit subdivided by the principle of magnetoelectricity (referred to as the 17-bit magnetic coding), its accuracy is not as good as that of the optical code disc. Even the magnetic coding has many modes, and the accuracy is also very different. This is because these high-bit resolution encoders are internally based on the high resolution obtained by the subdivision of the original signal sine and cosine signals. The encoder signal accuracy depends on the way the encoder original signal is obtained, signal quality and system accuracy, and Electronic error caused by subdivision and compensation.





