What is an encoder_what is the working principle of an encoder
What is an encoder_what is the working principle of an encoder
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts a signal (such as a bit stream) or data into a signal form that can be used for communication, transmission and storage. The encoder converts angular displacement or linear displacement into electrical signals. The former is called a code wheel and the latter is called a code ruler. Encoders can be divided into contact type and non-contact type according to the read-out mode; according to the working principle, encoders can be divided into two types: incremental and absolute. The incremental encoder converts the displacement into a periodic electric signal, and then converts this electric signal into a counting pulse, and the number of pulses represents the magnitude of the displacement. Each position of the absolute encoder corresponds to a certain digital code, so its indication is only related to the start and end positions of the measurement, and has nothing to do with the middle process of the measurement.
What is a code? For example, you need to give a phone number when you install a phone, and a postal code when you send a letter. These are all codes. Generally speaking, the process of representing a certain object or signal with numbers or certain words and symbols is called coding.
It is difficult to implement decimal encoding or encoding of certain characters and symbols with circuits. In digital circuits, binary codes are generally used. Binary only has two digits, 0 and 1, and several 0s and 1s can be arranged according to a certain rule to form different codes (binary numbers) to represent an object or signal. One-bit binary code has two kinds of 0 and 1, which can represent two signals; two-bit binary code has four kinds of 00, 01, 10, 11, which can represent four signals. n-bit binary code has
Kind, can represent
Signals. This kind of binary coding is easy to implement on the circuit. Only the binary-decimal encoder is discussed below.
The two-decimal encoder is a circuit that encodes the ten decimal numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 into binary codes. The input is 0-9 ten digits, and the output is the corresponding binary code. This binary code is also called two-decimal code, or BCD code for short. The encoding process is as follows:
1. Determine the number of bits of the binary code
Because the input has 10 digits and the 3-bit binary code has only 8 combinations, the output should be a 4-bit (take n=4) binary code. This type of encoder is usually called a 10/4-line encoder.
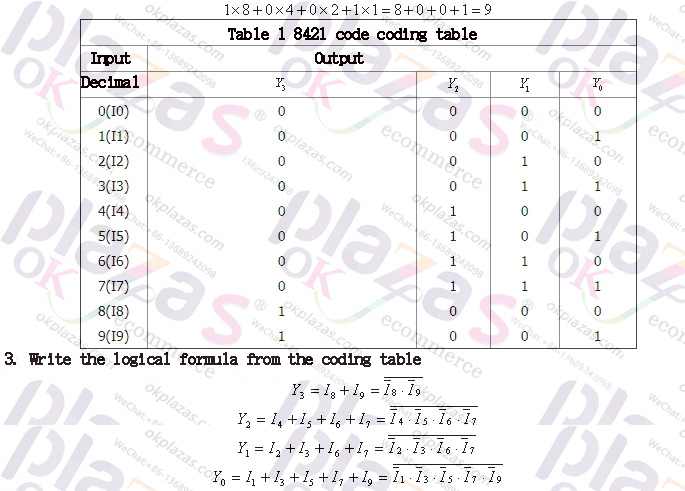
2. Column coding table
There are 16 states in 4-bit binary code, any of 10 states can represent ten digits from 0 to 9, and there are many solutions. The most commonly used is the 8421 encoding method, which is to take out the first 10 states from the 16 states of the 4-bit binary code, representing ten digits from 0 to 9, and remove the following 6 states, see Table 1. The decimal numbers represented by the 1s of each binary code are 8, 4, 2, 1, from high to low, which are called "weights", and then multiply each digit by the "weights" of each digit and add them to get the A decimal number represented by a binary code. For example, 1001, this binary code means
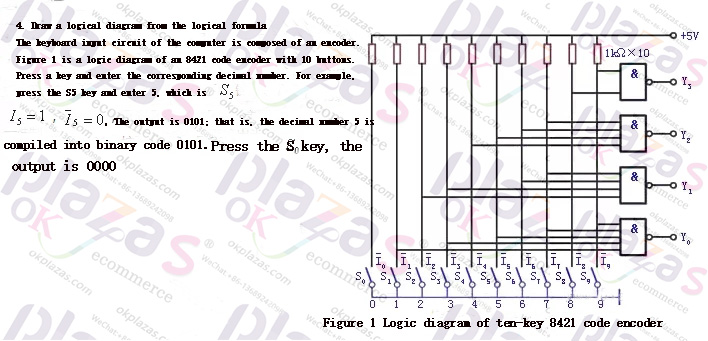
working principle:
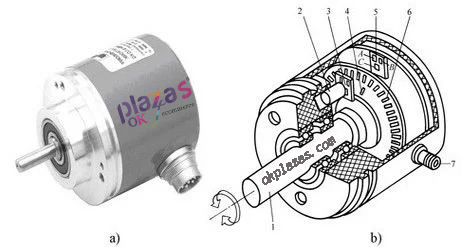
A photoelectric code disk with an axis in the center, on which there are circular and dark engraved lines, is read by photoelectric transmitter and receiver devices, and obtains four groups of sine wave signals combined into A, B, C, D, each sine wave Phase difference of 90 degrees (relative to a cycle of 360 degrees), the C and D signals are reversed and superimposed on the A and B phases to enhance the stable signal; in addition, a Z-phase pulse is output every revolution to represent the zero reference Bit.
Since the phases A and B differ by 90 degrees, the encoder's forward and reverse rotation can be judged by comparing the phase A or the B phase. The zero reference position of the encoder can be obtained through the zero pulse.
The materials of the encoder code disc are glass, metal, plastic. The glass code disc is deposited on the glass with very thin scribe lines, which has good thermal stability and high precision. The metal code disc is directly engraved with through and impassable lines and is not fragile. However, due to the certain thickness of metal, the accuracy is limited, and its thermal stability is one order of magnitude worse than that of glass. Plastic code discs are economical, and their cost is low, but accuracy, thermal stability, and life are worse.
Resolution-The number of open or dark engraved lines provided by the encoder per 360 degree rotation is called resolution, also known as resolution division, or directly called the number of lines, generally 5 to 10,000 lines per revolution.





