What is RTD thermal resistance
What is RTD thermal resistance What is the difference between two-wire and three-wire RTD
In the previous article, we introduced the principle of thermocouple temperature measurement, which uses the Seebeck effect to perform temperature measurement. In addition to thermocouples, RTD thermal resistance is often used in the industry for temperature measurement. Today in this article, we want to talk to you about what is RTD and how does it work?
The full English name of RTD is "Resistance Temperature Detector", so to be precise, it should be translated as "Resistance Temperature Detector". RTD is a special kind of resistance, its resistance will increase with the increase of temperature, and decrease with the decrease of temperature. The industry uses its characteristic for temperature measurement, so RTD is also commonly known as "thermal resistance".
Not all metals are suitable for RTD. Materials that meet this characteristic need to meet the following requirements:
1) The resistance of the metal has a linear relationship with temperature changes;
2) The metal is more sensitive to temperature changes, that is, the resistance change (temperature coefficient) caused by the unit temperature change is relatively large;
3) The metal can resist fatigue caused by temperature changes and has good durability; there are not many metals that meet this requirement. Common RTD materials include platinum (Pt), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu).
Taking platinum thermal resistance as an example, according to its resistance value, it can be divided into Pt50, Pt100,
Pt200, Pt500 and Pt1000 etc. The value in the name indicates the resistance of the thermal resistance at 0℃
value. For example: Pt100 means that the resistance value of the sensor at 0°C is 100Ω; while Pt1000 means that the resistance value of the sensor at 0°C is 1000Ω.
The resistance value of RTD thermal resistance at different temperatures can be approximated by the formula: R=R0(1+α T).
among them:
1) R0 represents the resistance value of RTD at 0℃;
2) α is called the temperature coefficient, which represents the change in resistance per unit temperature;
3) T represents the measurement temperature, the unit is ℃; according to the number of lead wires of the RTD thermal resistance
At the same time, RTD can be divided into two-wire system, three-wire system and four-wire system. The lead of the two-wire RTD is directly led out two wires at both ends of the resistor to the temperature measurement module. The temperature measurement module adopts the principle of bridge balance, and RTD is used as an arm of the bridge for measurement.
The schematic diagram of the two-wire RTD is as follows:
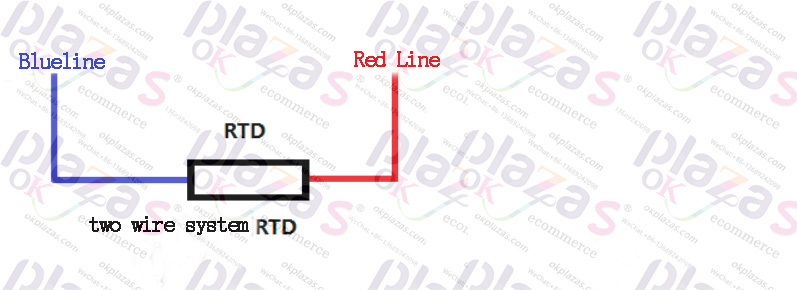
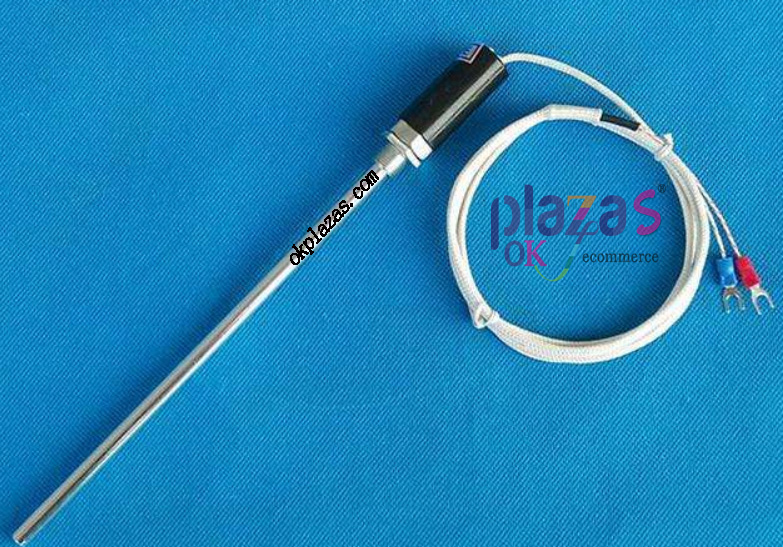
The two-wire RTD sensor does not consider the resistance of the lead wire, and the error is relatively large. It is only suitable for occasions with low accuracy requirements. The physical map of the two-wire RTD is as follows:

In order to eliminate the influence of RTD leads on the measurement results, many RTDs use a three-wire system. Three lines
The system is based on the two-wire system, and the third line is drawn from one end of the resistor, as shown in the figure below:
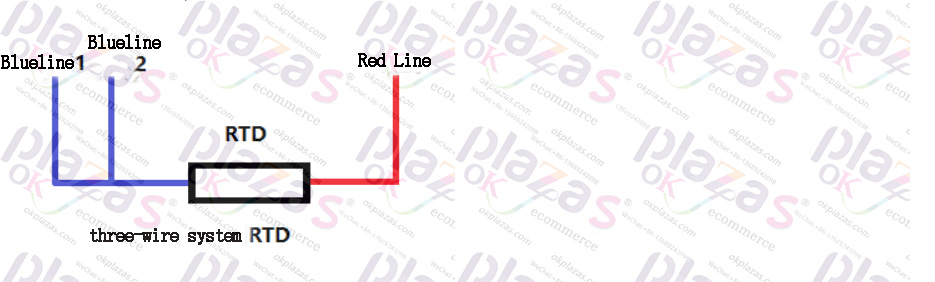
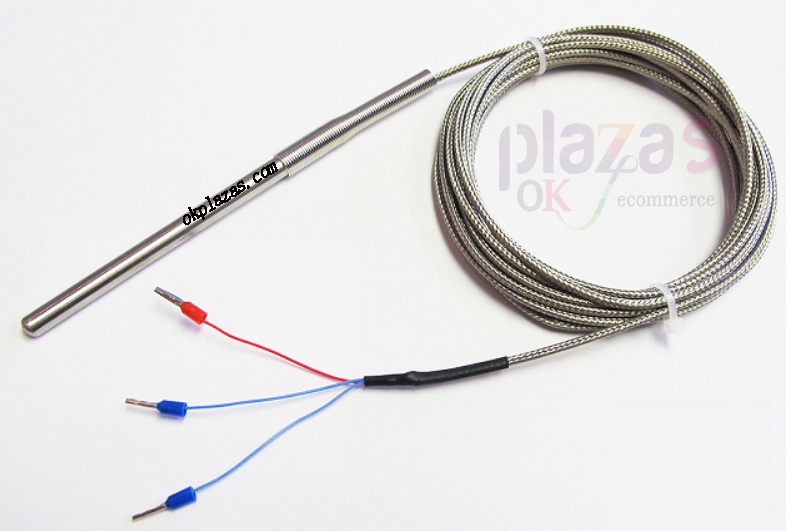
The three-wire RTD can eliminate the influence of the sensor lead itself on the measurement results to a large extent, and the detection accuracy is greatly improved compared with the two-wire system. The following picture is the physical picture of the three-wire RTD:

The four-wire RTD is based on the three-wire system and adds another line, that is, there are two lines at each end of the resistor, as shown in the figure below:
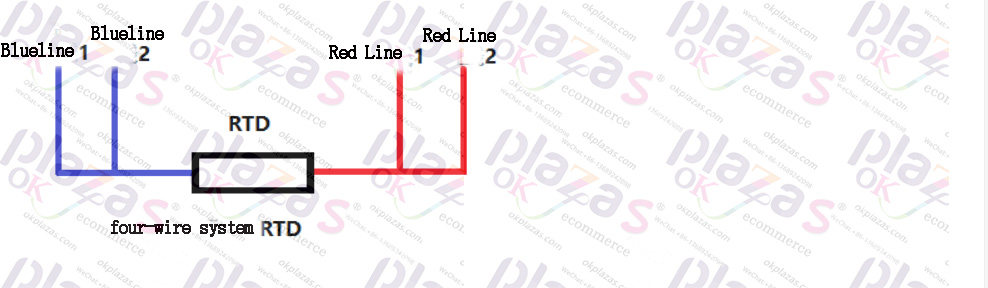
Four-wire RTD can completely eliminate the influence of lead resistance and has very high accuracy. It is generally used in laboratories or occasions that require high accuracy. The linearity of RTD is better than thermocouple, it is the most accurate and stable temperature sensor at present. However, since the change of resistance takes time, its response speed is slow. At the same time, its price is relatively expensive, which is suitable for occasions that have certain requirements on accuracy and poor cost control. Ok, let’s stop here for the RTD thermal resistance.





