Application of Hall effect encoder in BLDC motor field
Application of Hall effect encoder in BLDC motor field
In today's world, systems that require BLDC motors require higher accuracy than ever before in position measurement. The BLDC motor relies on an external controller to achieve commutation. The process of switching current in the motor phase to produce motion. Since the advent of the BLDC motor, the Hall effect sensor has always been the preferred solution for commutation feedback. A tight control loop is required. With high-precision position induction feedback, BLDC motors can stand out in many applications, and the BLDC motor application market is also growing.
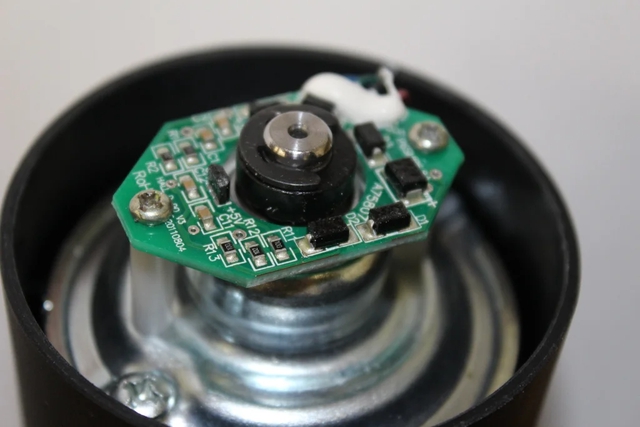

The Hall sensor rotary encoder is a very simple, cost-effective and robust method for measuring rotational motion. It uses non-contact magnetic induction by simply installing a multi-pole ring magnet on the rotating part and installing it to a nearby Hall effect sensor. To detect the speed and direction. The Hall array sensor passing through the magnetic field generates a signal and then interpolates it to the resolution. The magnetic phased array sensor is used to average the signals on multiple detectors to provide a powerful high-resolution signal. Standard, not sensitive to shock and vibration.
How Hall Effect Encoders Work
The Hall effect encoder uses a magnetic phased array, which contains Hall sensor elements, which are arranged in a matching manner with an electromagnetic wheel. The sensor generates a signal when passing through a magnetic field, and then interpolates the signal to the required resolution rate. This kind of magnetic phased array technology can now be used in IC chips, which integrate sensors and processors in the same chip, which significantly reduces the number of chips and the complexity of the PCB board, thus achieving robustness and compactness. Easy to manufacture, magnetic Hall phased array technology represents today's leading magnetic encoder technology.
The innovation of phased array technology has greatly improved the optical encoder technology. In the same way, the phased array system benefits from improving the resolution, compactness and reliability of the magnetic encoder system, and the data capture is distributed on multiple detectors. , The error is averaged and the sensitivity is improved.
Disadvantages of Hall Effect Encoders
In order for the controller to commutate effectively, it must always need accurate information about the rotor position, and unless paired with incremental encoders, they often cannot provide a complete motor position map. In a typical case, three-phase control requires three sensors, and the Hall-effect sensor is embedded in the stator of the motor to detect the rotor position, which is used to switch the transistor in the three-phase bridge to drive the motor. This position feedback method has some disadvantages. Although the cost of Hall-effect sensors is very low, the cost of integrating these sensors into the BLDC will double the total cost of the motor. In addition, the controller only obtains a partial position map of the motor from the Hall-effect sensor, which may require accurate position feedback for normal operation.
Hall effect encoder application field
Magnetic Hall-effect encoders are very rugged. Magnetic encoders are based on inductive effects. They do not require bearings, thereby eliminating the point of failure of the system. Generally, the electronic devices inside the Hall-effect encoder are encapsulated and they are not exposed to the components. Magnetic Hall-effect encoders can work under dust cover in sawmills, or in humid and watery environments, without any other protection.
Magnetic Hall-effect encoders output reliable digital feedback in the most demanding and demanding application environments. The application of this technology usually requires wide temperature specifications, high shock and vibration resistance, robust sealing, and protection against contaminants , But also pay attention to the reliability of the output signal, easy to install and reduce downtime. Popular applications for magnetic Hall-effect encoders include speed and position feedback in construction, agriculture, mining, forestry, and food and beverage applications with flushing fluids or corrosive chemicals.





