How does a stepper motor work What are its characteristics?
How does a stepper motor work What are its characteristics?
We will learn the following:
1) What is a stepper motor;
2) Some basic concepts related to stepper motors;
3) Classification and structure of stepper motors;
4) Features of stepping motor;
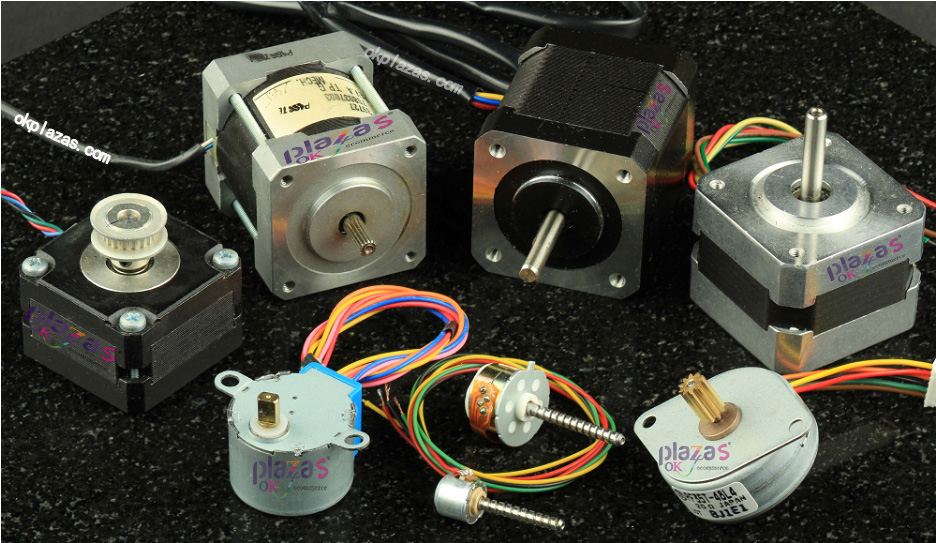

1.1 What is a stepper motor
Stepping motor is an open-loop control motor based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacement or linear displacement. It is a common actuator in industrial control systems (Note: Industrial control systems are controlled by controllers and Components, sensors and actuators).
The inside of a stepper motor is composed of a rotor and a stator. The picture below is the appearance of a two-phase stepper motor:
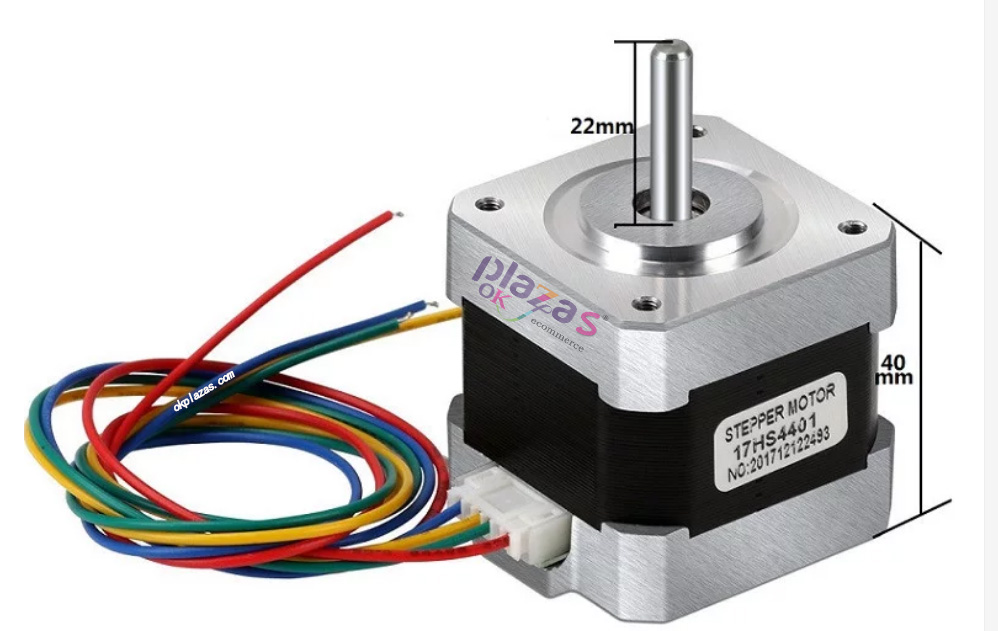
1.2 Basic concepts related to stepper motors
1.2.1. Number of phases: refers to the number of groups of the stator windings of the stepper motor (ie the number of internal coils). Commonly used are two-phase, three-phase, four-phase, and five-phase stepper motors;
1.2.2. Step angle: the angle the stepper motor rotates after receiving a pulse signal. The step angle has been determined when the motor leaves the factory and will be written on the motor. Generally, the step angle of a two-phase motor is 0.9°/1.8°, the step angle of a three-phase motor is 0.75°/1.5°, and the step angle of a five-phase motor is 0.36°/0.72°; if the subdivision driver is not used, The control requirement can only be met by selecting a stepping motor with non-synchronous pitch angle. The subdivision driver can change the step distance of the stepper motor
Angle, this we will introduce in the second section "Understanding the stepper driver"; 1.2.3, holding torque (holding torque): refers to the stepper motor winding is energized and the rotor is not rotating, so that the motor can move a complete step The required torque. The holding torque is mainly limited by the maximum current allowed by the motor windings, which is usually greater than the running torque. Holding torque is one of the most important parameters of a stepper motor. Its advantage is that it can keep the load at a certain position. Unless otherwise specified, the torque of a stepper motor usually refers to the holding torque. For example, the torque of a stepping motor is 3.5NM, which means that its holding torque is 3.5NM;
1.2.4, damping torque (detenttorque): refers to the torque generated by the mechanical characteristics (permanent magnetic structure) of the stepper motor winding when it is not energized. When the power is off, you can feel the damping torque by turning the rotor by hand;
1.3 Classification and structure of stepper motors
The inside of a stepper motor is composed of a rotor and a stator.
When the stator coil is energized, it will generate an induced magnetic field. The induced magnetic field interacts with the rotor to make the rotor
Turn a certain angle. According to the different excitation methods, stepper motors can be divided into three types: permanent magnet type, reactive type (reluctance type) and hybrid type
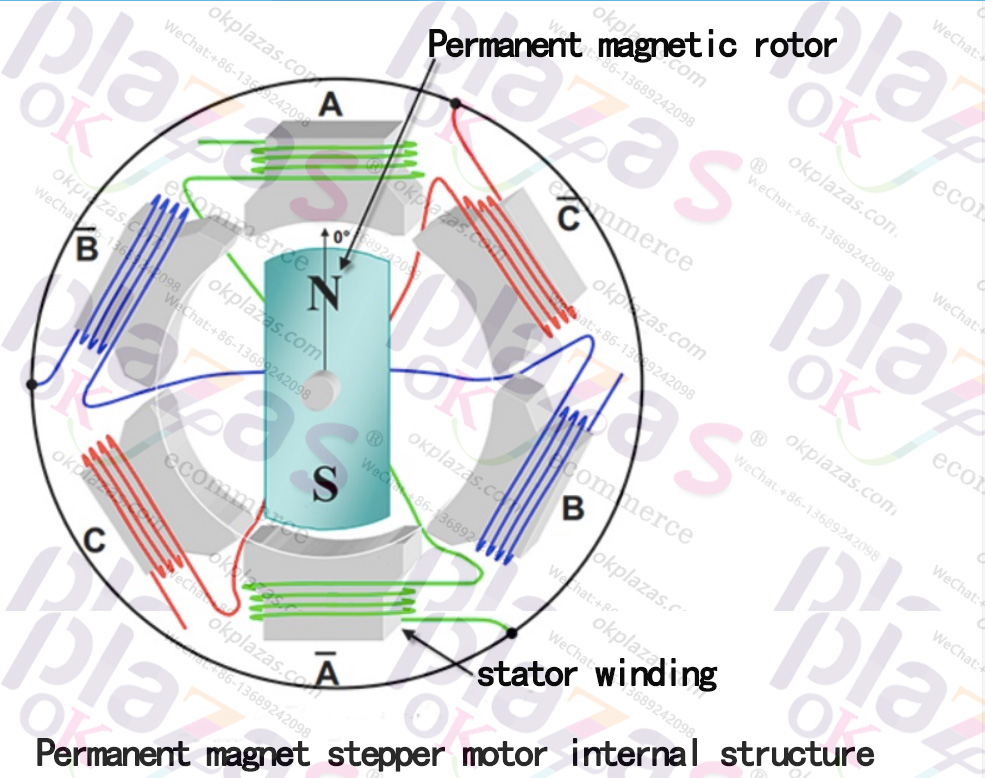
1.3.1, permanent magnet type (permanent magnet stepper motor)
The rotor of a permanent magnet stepping motor is a permanent magnetic, cylindrical structure with N poles and S poles; the stator is an excitation coil with a symmetrical structure; when the stator coil is energized with direct current, according to Ampere’s right hand law, A magnetic field is generated at both ends of the coil; the magnetic field generated by the stator interacts with the permanent magnetic material of the rotor to turn the rotor. By energizing the stator windings alternately, the rotor can be controlled to alternately move in a certain direction;
the stator/rotor structure of a permanent magnet stepping motor is shown in the figure below:
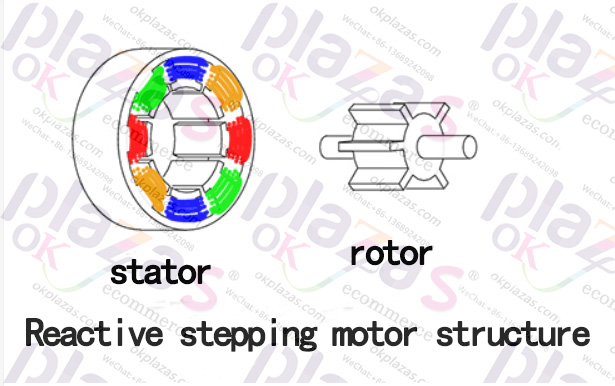
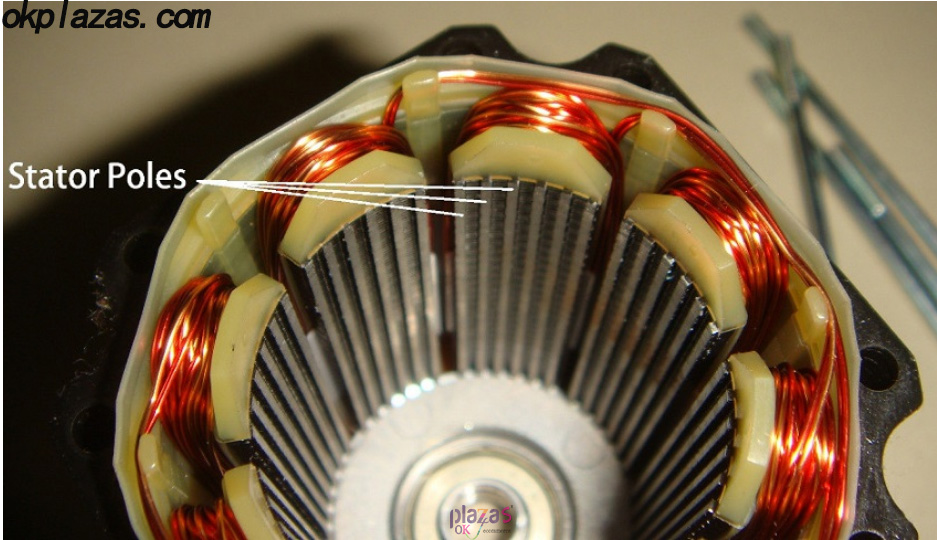
1.3.2, reaction type (variablereluctance stepper motor)
Reactive stepping motor is also called reluctance stepping motor. Its rotor is a non-magnetic, soft-iron, tooth-like structure; its stator is composed of excitation coils; because the rotor is a non-magnetic structure, there is no electricity in the stator Before, there was no magnetic interaction between the stator and the rotor. Therefore, the reactive stepper motor has no detent torque.
The internal structure diagram of the reactive stepping motor is as follows:
1.3.3 Hybrid (hybrid steppermotor) As the name implies, hybrid stepper motors combine the advantages of permanent magnet and reactive stepper motors. Its rotor uses permanent magnet materials and divides it into a south pole (S pole) and a north pole. (N pole) Two parts, each part has many tooth-like structures, as shown in the following figure:
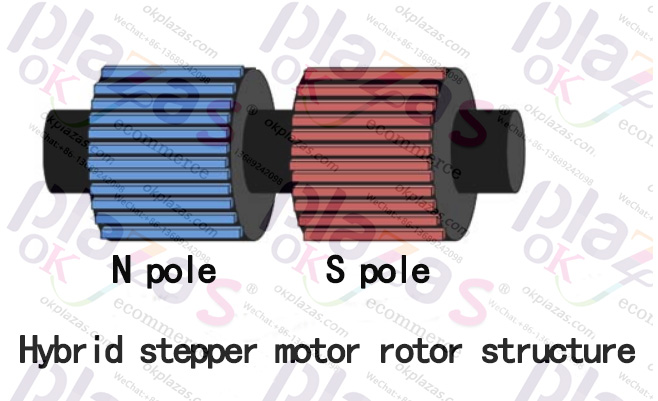
The stator of the hybrid stepping motor is composed of excitation coils, and each group of coils also has alternately distributed tooth-like structures. As shown below:

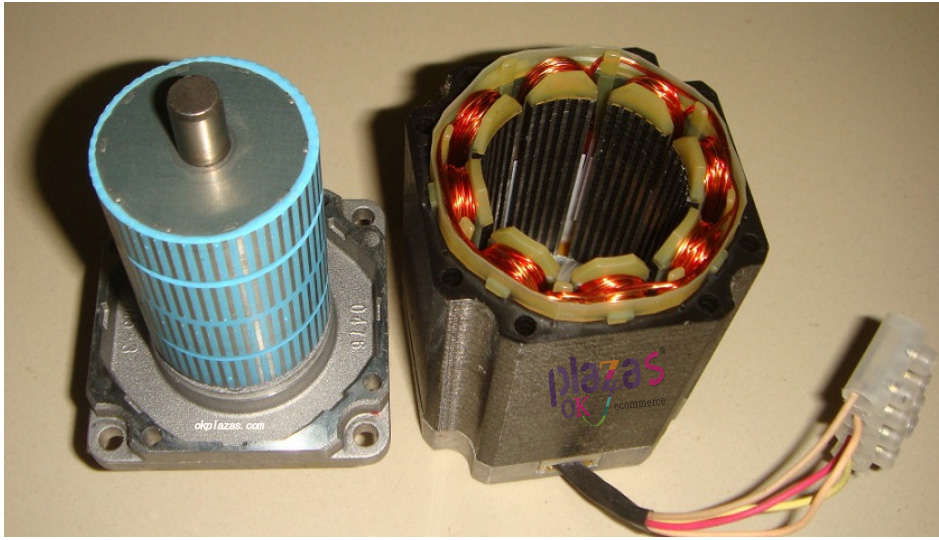
The hybrid stepping motor has a small step angle and good dynamic performance. It is the most widely used stepping motor. The following picture is a physical picture of the rotor and stator of a hybrid stepping motor:

1.4 Features of stepper motor
The stepping motor is simple in structure, easy to use, has no accumulated error, and only needs pulse signals to work. Therefore, it can be controlled by PLC or a device that can generate pulse signals such as a single-chip microcomputer. It can be used in industrial automation control. Very extensive.
However, its noise and vibration are large, and it may be out of step, so it is only suitable for occasions with low accuracy requirements.
In addition, the position and speed signals of the stepper motor cannot be fed back to the control system, and generally can only be used for open loop control. If you want to form a closed-loop control system, you need to add signal feedback devices such as encoders on the motion axis.





