What is the Safe Torque Off of the inverter
What is the Safe Torque Off of the inverter
AC asynchronous motors play an important role in today's industrial production, and the speed regulation and control of the motors are often completed by frequency converters. In daily production, we hope that the performance of the motor is safe and reliable. This safety and reliability is manifested in two aspects:
1) It can brake quickly in an emergency;
2) Cannot start when the safety conditions are not met. Since the control of the motor comes from the inverter,
This inverter must meet the corresponding safety requirements. During the commissioning or use of the inverter, it is sometimes found that the inverter is in a "safe stop" state. What is "safe stop"? Under what circumstances will the inverter be in a "safe stop" state?
In today’s article, we will take SEW’s MDX60B/61B series inverter as an example.
Let's talk about the "safe stop" of the inverter.

The English name of "safe stop" is "Safe Torque OFF (STO)", literally translated as "safe torque off". "Safe stop" is a state, not a malfunction. When the safe stop (STO) function is activated, the inverter cuts off the power supply to the motor, and the motor loses power and cannot output torque, so it cannot start. In SEW's MDX60B/61B series inverter, if its safe stop function is
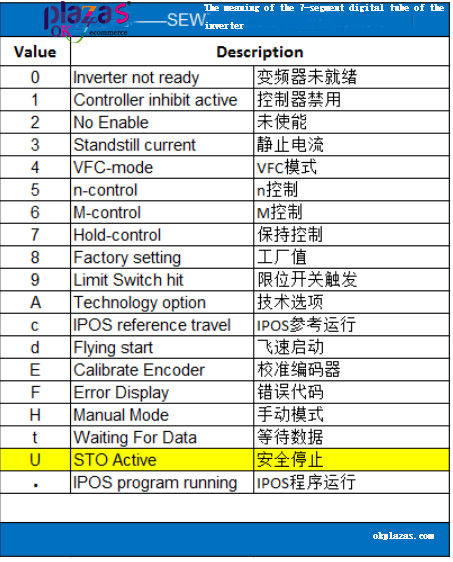
activated, the 7-segment digital tube will display "U", and the panel of the handle will
The words "safe stop" are displayed, as shown in the figure below:

The meaning of the 7-segment digital tube of the inverter is as follows:
So, how is the safety stop function activated?
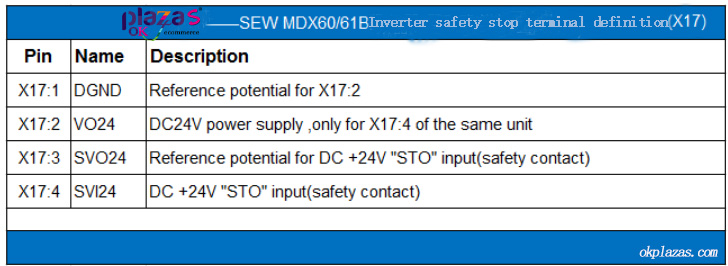
SEW MDX60/61B series inverters integrate safety relays (Safety contact), which can be used to disable or activate the safety stop function. The wiring terminal of the safety relay is X17. When the No. 4 terminal (X17:4) of X17 is connected to the positive pole of DC 24V and the No. 3 terminal (X17:3) is connected to the negative pole of DC 24V, the safety stop function is disabled. If X17:4 has no DC +24V input, the safe stop function is activated.
In other words, before the inverter works normally, X17:4 must be provided with a DC 24V input signal.
Otherwise, the inverter will be in a safe stop state and cannot work.
The terminal definition of safety relay X17 is shown in the following table:
In addition to using the safety relay that comes with the inverter, MDX60B/61B also provides a dedicated safety module: MOVISAFE DCSxB series. Dedicated safety modules can provide options to meet different safety levels, with many safety functions, such as: STO (Safe Torque Off), SS1 (Safe Stop 1), SS2 (Safe Stop 2), SOS (Safe Operating Stop), SLS (Safely Limited Speed), etc. We have the opportunity to talk in detail. Most inverters actually have a safe stop function. For example, the Siemens G120 series can activate the safe stop function through fail-safe input terminals or PROFIsafe. However, the configuration of the safe stop function requires the use of an operation panel or STARTER software, which is relatively complicated.
Ok, let’s talk about the safe stop of the inverter (Safe Torque Off, STO).





